AI-Driven Personalisation in Composable Commerce: Beyond Product Recommendations
The phrase “customers who bought this also bought” is two decades old. Product recommendation engines were among the earliest commercial applications of machine learning, and they remain valuable. But in 2025, reducing AI-driven personalisation to product recommendations is like reducing a smartphone to a telephone. The technology has moved far beyond its original application. AI research has driven the evolution of personalisation techniques, enabling far more sophisticated and context-aware experiences than early recommendation engines could provide.
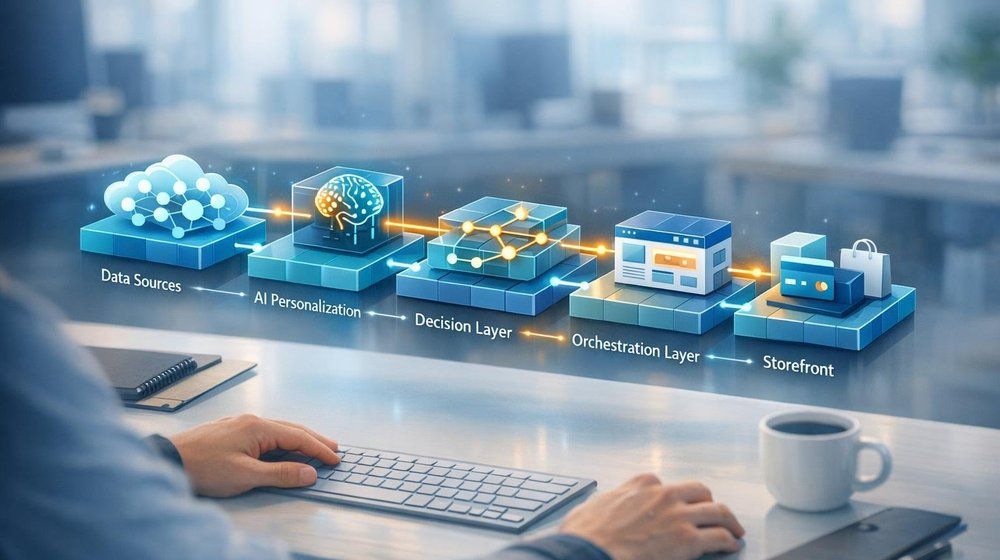
For enterprises running composable commerce architectures — particularly those built on Elastic Path — AI personalisation now spans the entire customer journey: from how products are discovered through AI-powered search, to how prices are optimised in real time, to how content is merchandised for individual visitors, to how conversational AI assistants guide buyers through complex purchasing decisions. Capabilities that were once the domain of science fiction are now being realized in composable commerce through advanced artificial intelligence.
This article explores how AI capabilities are transforming personalisation within composable commerce architectures and the integration patterns that make it work.
Why Composable Commerce Is Uniquely Suited to AI Personalisation
Monolithic commerce platforms, often referred to as legacy platforms, bundle everything — search, recommendations, pricing, content — into a single system. These legacy platforms can hinder growth and adaptability in today’s evolving e-commerce landscape. Adding AI personalisation typically means working within the platform’s constraints: limited model choices, restricted data access, and rigid integration points. Traditional ecommerce platforms also face challenges in meeting modern security and compliance standards, making it harder to implement advanced features securely.
Composable commerce architectures take the opposite approach. Each capability is a separate, API-first service that can be independently selected, deployed, and evolved. This modularity is precisely what AI personalisation requires, because:
-
Model flexibility: You can choose the best AI model for each personalisation use case rather than accepting a platform vendor’s built-in model.
-
Data access: API-first architecture makes it straightforward to feed AI models with data from across the commerce ecosystem — catalogue data from Elastic Path’s PXM (Product Experience Management), behavioural data from analytics services, CRM data from customer platforms.
-
Rapid iteration: AI models improve through experimentation. Composable architecture allows you to swap, test, and update personalisation services without touching the rest of the commerce stack.
AI-Powered Search: From Keywords to Understanding
Traditional ecommerce search is keyword-based. A customer types “blue running shoes size 10” and the search engine matches those tokens against product attributes. The approach works for specific queries but fails badly for exploratory or natural language queries. AI-powered search engines analyze data from both user queries and product catalogs to improve the relevance and accuracy of search results.
AI-powered search using embedding models and large language models transforms this experience by understanding and processing human language, enabling the system to interpret intent and context far beyond simple keyword matching.
Semantic Search
Semantic search uses embedding models to understand the meaning behind a query, not just the words. When a customer searches for “something to keep my laptop dry on my commute,” a semantic search engine understands the intent and returns waterproof laptop bags and sleeves — even though none of those keywords appear in the query.
In a composable architecture, implementing semantic search involves:
-
Embedding generation: Processing the product catalogue through an embedding model to create vector representations of each product. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of product descriptions, attributes, and categories, and enable the detection of complex patterns in product data.
-
Vector storage: Storing the embeddings in a vector database (such as Pinecone, Weaviate, or Azure AI Search) that supports similarity search.
-
Query processing: Converting the customer’s search query into an embedding and finding the most similar product embeddings. Embedding models can identify complex patterns in customer queries, allowing for more accurate matching with relevant products.
-
Result ranking: Combining semantic similarity scores with business rules (stock availability, margin, promotional priority) to produce the final ranked results.
The composable architecture means the search service connects to Elastic Path’s product catalogue via API, processes it independently, and returns results that the frontend renders. The search service can be updated, retrained, or even replaced without modifying the commerce platform.
Semantic search has real-world applications in eCommerce, improving product discovery and customer satisfaction by delivering more relevant search results.
Conversational Commerce
Taking AI-powered search further, conversational commerce uses LLMs to create AI shopping assistants that engage customers in natural dialogue:
-
“I need a gift for my partner who likes hiking and cooking.”
-
“What is the difference between your Professional and Enterprise plans?”
-
“I bought the starter kit last month — what should I add next?”
These interactions require the AI to understand context, access product data, consider customer history, and generate helpful responses. In a composable architecture, the conversational AI service connects to multiple backend services — the product catalogue, the customer profile, the order history — through their respective APIs.
Dynamic Pricing Optimisation with Machine Learning
AI-driven pricing moves beyond static price lists and basic promotional discounts. Machine learning models analyse demand patterns, competitive pricing, inventory levels, customer segments, and real-time market conditions to optimise prices dynamically. These AI pricing models rely on large volumes of training data to learn pricing patterns and generate accurate recommendations. AI-driven pricing is also a form of advanced problem solving, addressing the complexity of B2B pricing scenarios through logic-based approaches and reasoning methods.
In B2B composable commerce, where pricing is already complex (tiered pricing, contract pricing, volume discounts, currency variations), AI pricing optimisation adds another layer:
-
Demand-responsive pricing: Adjusting prices based on real-time demand signals, similar to airline or hotel pricing but applied to B2B product catalogues.
-
Customer-specific pricing: Using AI to determine the optimal price point for each customer based on their purchasing history, contract terms, and price sensitivity.
-
Promotional optimisation: Predicting which promotional offers will drive the highest conversion or margin improvement for specific customer segments.
Elastic Path’s pricing engine supports the complex pricing rules that B2B requires — currency, tiers, customer groups — and its API-first design allows an external AI pricing service to feed optimised prices into the platform.
Personalised Content Merchandising
Content merchandising — the strategic placement of editorial content, promotional banners, and category descriptions throughout the commerce experience — has traditionally been manual. Merchandising teams decide which content appears where, for how long, and for which audience.
AI personalisation automates and optimises this process:
-
Behavioural targeting: Showing different hero banners, product collections, and editorial content based on the visitor’s browsing history, referral source, and predicted interests. AI can personalise content for different products and services offered by the business, ensuring that each visitor sees the most relevant offerings.
-
A/B test automation: Running continuous experiments across content placements and using AI to automatically allocate traffic to winning variants.
-
Content generation: Using LLMs to generate personalised product descriptions, category page introductions, and email content tailored to specific customer segments.
AI-driven merchandising also helps identify and engage potential customers by delivering tailored content and offers that match their interests and needs.
In a composable architecture, the content personalisation engine sits between the headless CMS (where editorial content is managed) and the frontend (where it is rendered). The engine decides, in real time, which content variant to serve to each visitor.
Elastic Path AI Product Recommendations: Architecture Patterns
While this article argues that personalisation extends far beyond recommendations, product recommendations remain a core capability. Advanced AI algorithms power these product recommendation systems, enabling more accurate and relevant suggestions for users. Within the Elastic Path ecosystem, implementing AI product recommendations follows a clean architectural pattern:
Data Pipeline
-
Catalogue sync: Product data from Elastic Path PXM is synchronised to the recommendation engine, including product attributes, categories, pricing, and availability.
-
Behavioural collection: A client-side tracking service captures user interactions — page views, searches, add-to-cart events, purchases — and sends them to the recommendation engine.
-
Model training: The recommendation engine trains models on the combined product and behavioural data. Common model types include collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, and hybrid approaches. The engine improves its accuracy through knowledge gained from historical data, allowing it to learn and adapt over time. Additionally, recommendation models can be tailored to the unique needs of each business industry, ensuring that suggestions are relevant to the specific context and audience of the eCommerce website.
Serving Recommendations
The recommendation engine exposes an API that the frontend calls with context (current product, current customer, current cart) and receives ranked product recommendations in response. The frontend renders these within the page layout of the eCommerce store, pulling full product details from Elastic Path’s API.
Beyond Collaborative Filtering: Generative AI Approaches
Modern recommendation engines go beyond traditional collaborative filtering (“customers who bought X also bought Y”) by incorporating:
-
Session-based recommendations: Using the current browsing session’s behaviour, even for anonymous visitors.
-
Context-aware recommendations: Considering time of day, device type, geographic location, and referral source.
-
LLM-enhanced recommendations: Using large language models to understand product relationships that statistical models miss — for example, recommending a specific mounting bracket because the product description mentions it is required for wall installation. Modern recommendation systems often leverage deep neural networks and artificial neural networks, which are types of neural networks inspired by biological systems. These models consist of multiple layers that progressively extract higher-level features from raw data, enabling complex pattern recognition and deep learning. Gen AI models, such as large language models, are increasingly used to enhance recommendation quality by generating more relevant and context-aware suggestions.
Integration Architecture for Ecommerce Platforms
Bringing all of these AI personalisation capabilities together in a composable architecture requires careful integration design. Cloud computing platforms, such as Google Cloud, provide the scalable infrastructure and computing power necessary to support advanced AI personalisation at scale. These services are underpinned by robust data centers, which deliver the high availability and energy management required for enterprise-grade AI solutions. The key principles are:
Composable architecture allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing requirements, ensuring agility and future-proofing as technology and buyer behaviours evolve.
API Orchestration Layer
An API orchestration layer (often implemented as a Backend-for-Frontend or BFF) coordinates requests across the various services — Elastic Path for catalogue and cart, the search engine for product discovery, the recommendation engine for personalised suggestions, the CMS for content. This layer assembles the personalised page experience from multiple service responses.
Event-Driven Data Flow
AI models need data to learn from. An event-driven architecture (using message queues or event streams) ensures that user interactions, order completions, and catalogue changes flow to all AI services in near-real time. This keeps models current without creating tight coupling between services.
Fallback Strategies
AI services can fail or return degraded results. A robust architecture includes fallback strategies — showing trending products if the recommendation engine is unavailable, falling back to keyword search if semantic search fails, using default pricing if the pricing optimisation service is unreachable.
For enterprises running Elastic Path or planning a composable commerce implementation, adding AI personalisation is a natural evolution. The composable architecture already provides the API-first foundation that AI services require.
The practical starting point depends on your current capabilities and priorities:
-
If search conversion is low: Start with AI-powered search. The impact on product discovery is immediate and measurable.
-
If average order value is stagnant: Implement AI product recommendations beyond basic collaborative filtering.
-
If content merchandising is manual and slow: Add a personalisation engine between your CMS and frontend.
-
If pricing is complex and margin is under pressure: Explore AI-driven pricing optimisation.
McKenna Consultants works at the intersection of composable commerce and AI, with deep expertise in Elastic Path implementations and AI integration architecture. If you are evaluating AI-driven personalisation for your composable commerce platform, to discuss your strategy.
Agentic AI and Customer Experience
Agentic AI represents a new frontier in artificial intelligence, focusing on the development of autonomous AI systems—known as AI agents—that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and pursue specific goals with minimal human intervention. In the context of digital commerce, agentic AI is poised to transform the customer experience, enabling e commerce businesses to deliver highly differentiated and seamless interactions across every touchpoint.
Unlike traditional AI tools that perform specific tasks, agentic AI agents leverage advanced machine learning and deep learning techniques to analyze customer data, understand preferences, and adapt their behavior in real time. For example, an online store can deploy virtual assistants powered by agentic AI to guide customers through product discovery, answer complex questions, and facilitate online purchases—all while learning from each interaction to improve future performance.
The integration of agentic AI with generative AI tools unlocks even more possibilities. Generative AI applications can create personalized content, such as tailored product descriptions or dynamic marketing messages, while agentic AI ensures these assets are delivered at the right moment in the customer journey. This synergy enables organizations to offer immersive experiences like virtual try-ons, interactive product demos, and real-time support, driving higher engagement and boosting online sales.
Composable commerce offers the ideal foundation for adopting agentic AI. Its modular, API-first architecture allows businesses to seamlessly integrate new AI systems and generative AI applications without disrupting existing e commerce infrastructure. This flexibility empowers e commerce businesses to respond rapidly to changing customer demands and stay ahead of ecommerce trends.
Key applications of agentic AI in digital commerce include:
-
Personalized product recommendations: AI agents analyze customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history to suggest relevant products, increasing the likelihood of online purchases and maximizing the value of each customer interaction.
-
Virtual customer support: Agentic AI enables always-on virtual assistants that can resolve common queries, provide order updates, and escalate complex issues to human agents when necessary, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
-
Streamlined checkout processes: AI-driven systems can identify and remove friction points in the checkout flow, reducing cart abandonment and optimizing the entire process for higher conversion rates.
-
Social media engagement: AI agents can monitor social media apps, respond to customer inquiries, and generate engaging content, helping businesses attract customers and build stronger relationships across digital channels.
As AI researchers continue to advance the capabilities of agentic AI, the potential for innovation in e commerce and digital commerce will only grow. By embracing these new technologies and leveraging the flexibility that composable commerce offers, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving ecommerce business landscape.